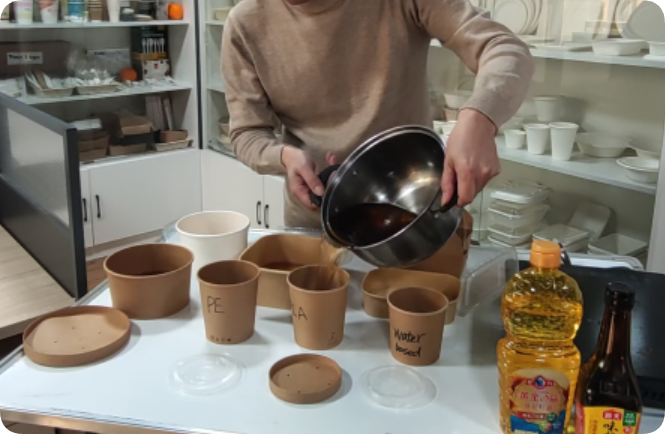












Compostable plastic spoons and forks are typically made from plant-based materials such as cornstarch, PLA (polylactic acid), or CPLA — PE vs PLA paper cups. These materials are biodegradable and designed to break down into natural elements in composting environments.
Individually wrapped plastic cutlery ensures high levels of hygiene, protects against contamination, and provides a convenient and sanitary solution for foodservice environments , PE vs PLA paper cups.
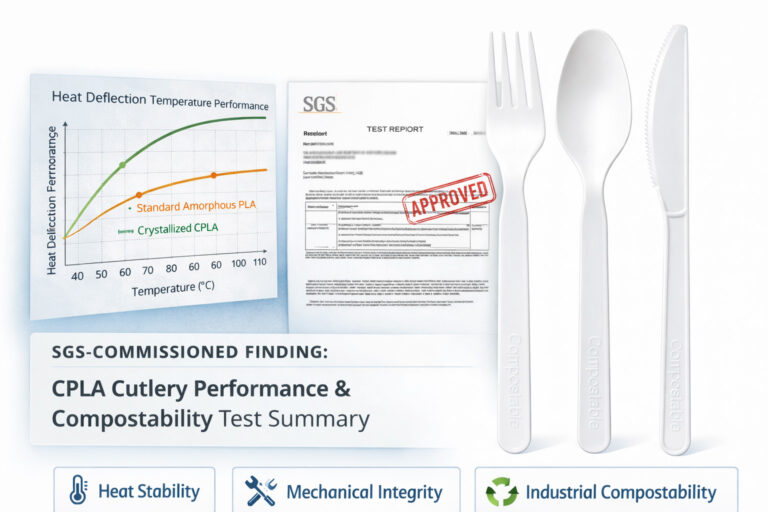
工業用コンポストの条件下では、素材や地域のコンポスト基準にもよるが、ほとんどのエコ・フレンドリー・カトラリーは90~180日で分解する。
Regulatory Factor PE Lining PLA Lining Aqueous Barrier* Classified as plastic under SUPD Yes Yes Formulation-dependent Mandatory marking Yes Yes Market-dependent EPR inclusion Yes Yes Likely reduced in some cases Branding friction High Moderate Lower Policy tightening risk High Moderate Lower Long-term compliance stability Weak Moderate Stronger *Note: Aqueous classification depends on polymer composition and national interpretation. The model illustrates a core reality: PLA no longer reduces compliance exposure relative to PE. Its advantages must therefore be justified on lifecycle or carbon grounds rather than regulatory grounds. 5.
To contextualize distributor concerns, Bioleader® developed an internal compliance exposure model comparing PE, PLA, and aqueous-coated cups — PE vs PLA paper cups.




Jゼロ・ウェイスト・パッケージングを目指す世界的な運動に参加する。
バイオリーダー を提供している:
📦 大量注文のサポートと迅速な配達
✍️ カスタムブランディングとOEMソリューション
🌍 世界的なエコ包装への対応
カタログを入手 製品リスト & お問い合わせ👉
Copyright © 2015-2026 厦門生物リーダー環境保護有限公司|無断複写・転載を禁じます。. プライバシーポリシー | AIポリシー | サイトマップ
WhatsAppはこちら